Which Two Structures of Plants and Fungi Perform Similar Functions
They act as antimicrobials and perform the role of. Cells of plants fungi animals and protists.

Risultati Immagini Per Damaged Hyphae Fungi What Is Fungi Plant Leaves
However Hawker 1965 holds that the cristae of fungal mitochondria are fewer flatter and more irregular.
. The mitochondria function as the power house of the cell. They are now placed in a separate kingdom Fungi. Over a period of.
The cells can be divided into two major groups Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. All land plants except Bryophytes mosses liverworts and hornworts have true roots. In majority of ascomycetes the common mode of asexual reproduction is through the formation of conidia singular-conidium.
Having evolved from aquatic ancestors Plants have subsequently migrated over the entire surface of the Earth. Like plants fungi often grow in soil and in the case. There is no fundamental difference between the mitochondria of fungi and those of green plants.
Initially it wasnt clear whether carnivorous plants made the enzymes themselves or if microbes living in their. To overcome this limitation some fungi such as Armillaria form rhizomorphs which resemble and perform functions similar to the roots of plants. Conidia are non.
The difference between both the cells are explained below. Chlorophyll fluorescence is used to measure the physiological state of plants using handheld devices that can measure photosynthesis linear electron flux and CO 2 assimilation by directly scanning leaves or by using reconnaissance imaging from a. As eukaryotes fungi possess a biosynthetic pathway for producing terpenes that uses mevalonic acid and pyrophosphate as chemical building blocks.
Plants are a source of food for all the Animals and other Plants either directly or indirectly. The Fungi however uniformly lack Chlorophyll heterotrophic and are chemically distinct from the Plants. Oidia stage similar to yeast is found.
The oviducts or fallopian tubes extend from the uterus to the ovaries but they are not in direct physical contact with the ovariesThe ends of the oviducts flare out into a trumpet-like structure and have a fringe of finger-like projections called fimbriae. Roots or root-like structures anchor plants to the soil andin plants with true roots serve as conduits for water absorption. The two most studied molecules are chlorophyll orangered fluorescence and lignin bluegreen fluorescence.
Simple compartments called vesicles and vacuoles can form by budding off other membranesMany cells ingest food and other materials through a process of endocytosis where the outer membrane invaginates and then pinches off to form a vesicle. Back in the 1970s researchers recognized that the digestive fluid they found in traps contained enzymes that functioned in very similar ways to many of the chemical weapons that plants wield against harmful bacteria fungi and hungry herbivorous insects. In some other ascomycetes as well.
Stomata or similar structures are necessary in land plants because the waxy cuticle blocks free-flow of gasses. Eukaryote cells include a variety of membrane-bound structures collectively referred to as the endomembrane system. Let us have a detailed look at the plant cell its structure and the.
In yeasts asexual reproduction occurs through budding and fission. When an egg is released at ovulation the fimbrae help the egg enter into the tube and passage to the uterus. Cell without a well-defined nucleus ie.
Motile structures do not occur in the life cycle. They induce flowering fruit set and abscission maintain perennial growth or signal deciduous behaviour. The cristae contain the same fluid that fills the space between the two membranes.
These small molecules exert a wide range of effects on the plant itself and on other living organisms. Cell with a well-defined nucleus ie. Secondary metabolites are substances manufactured by plants that make them competitive in their own environment.

Plant Vs Animal Cells Venn Diagram For Educational Purposes Venn Diagram Plant And Animal Cells Animal Cell Cell Biology Notes

How Are Plant Cells Different Than Fungi Cells Earth Com

Protists And Fungi Protists Plant Diseases Fungi

Plants Gardening Plants Fruits Fleshy Fruit Berry Fruit 1 Image Visual Dictionary Online Berry Fruit Grape Berry Fruit

Internal Structure Of The Dicot Root By Openstax Jobilize Llc Root Diagram Parts Of A Flower Plant Tissue

Mushroom Body Structure Mushroom Lifecycle Information About Mushrooms Mushrooms 101 Stuffed Mushrooms Kingdom Fungi Plant Pathology
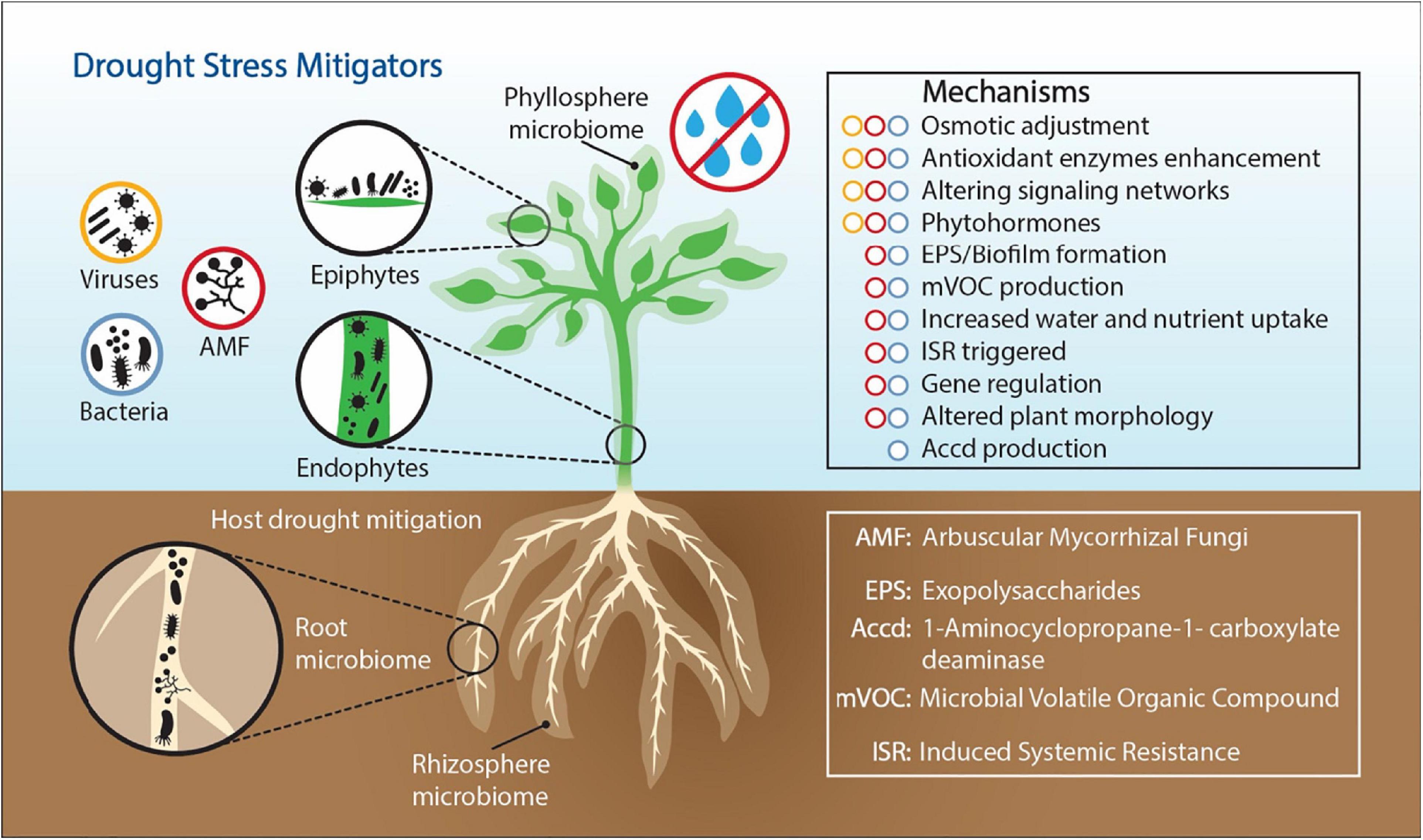
Frontiers The Role Of Plant Associated Bacteria Fungi And Viruses In Drought Stress Mitigation Microbiology

Internal Structure Of Dicot And Monocot Seeds 10 Commandments Earth Science Seeds
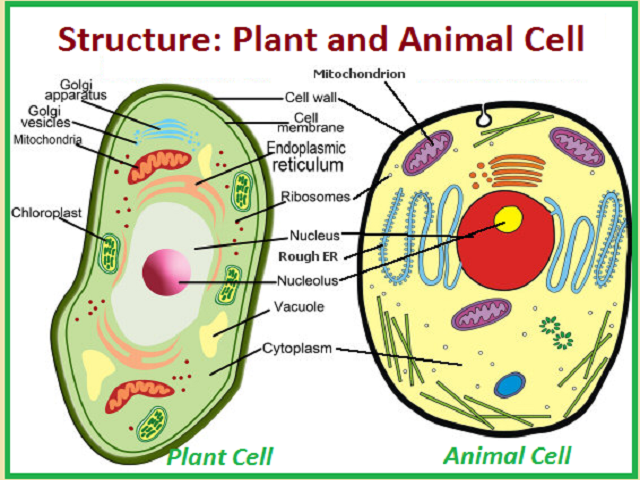
What Is The Structure Of Plant And Animal Cells

Simply Fungi The Lifecycle Of A Mushroom Fungi Stuffed Mushrooms Scientific Drawing

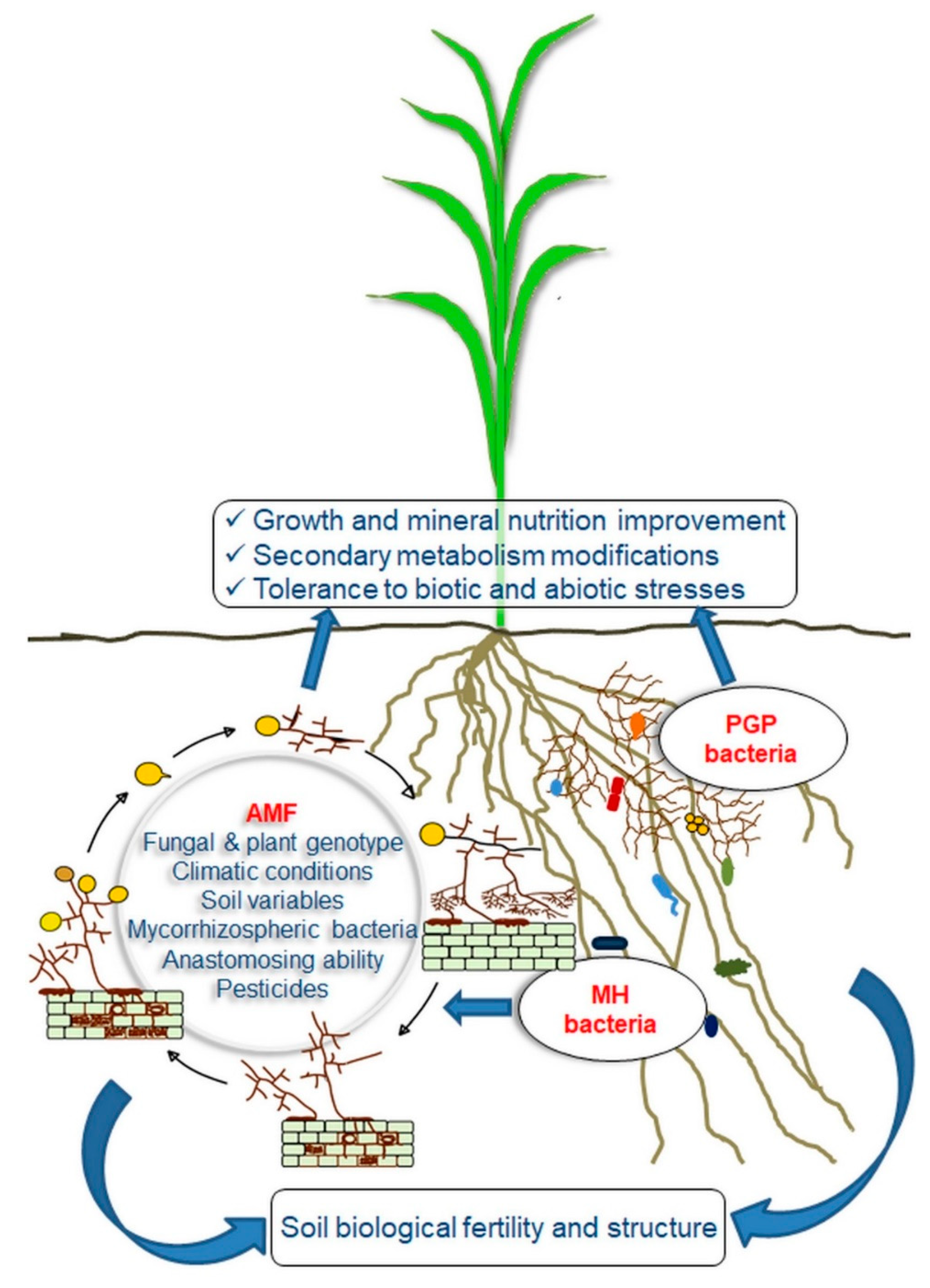
Agronomy Free Full Text Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi And Associated Microbiota As Plant Biostimulants Research Strategies For The Selection Of The Best Performing Inocula Html

Hyphae Production Structure Morphology Types Fungi Fungus Body Cell Wall

Plant Stems And Their Structure Biology Plants Plant Science Teaching Biology

Label The Parts Of A Mushroom Parts Of A Mushroom Stuffed Mushrooms Homeschool Science

Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Cells Main Differences Prokaryotic Cell Cell Prokaryotes



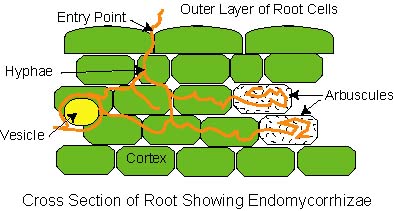
Comments
Post a Comment